What are Endocannabinoids?
Written by: Ruby Deevoy
CBD oil is a very unusual supplement, in that it has a vast array of mechanisms through which it works in the body. In fact, a whopping 65 molecular targets have been discovered for CBD alone, and they just seem to keep on coming. While all of these play vital roles in the effects CBD has (explaining in a nutshell how CBD can affect so many different things), it’s perhaps the interaction with the endocannabinoid system that has the most over-arching impact.
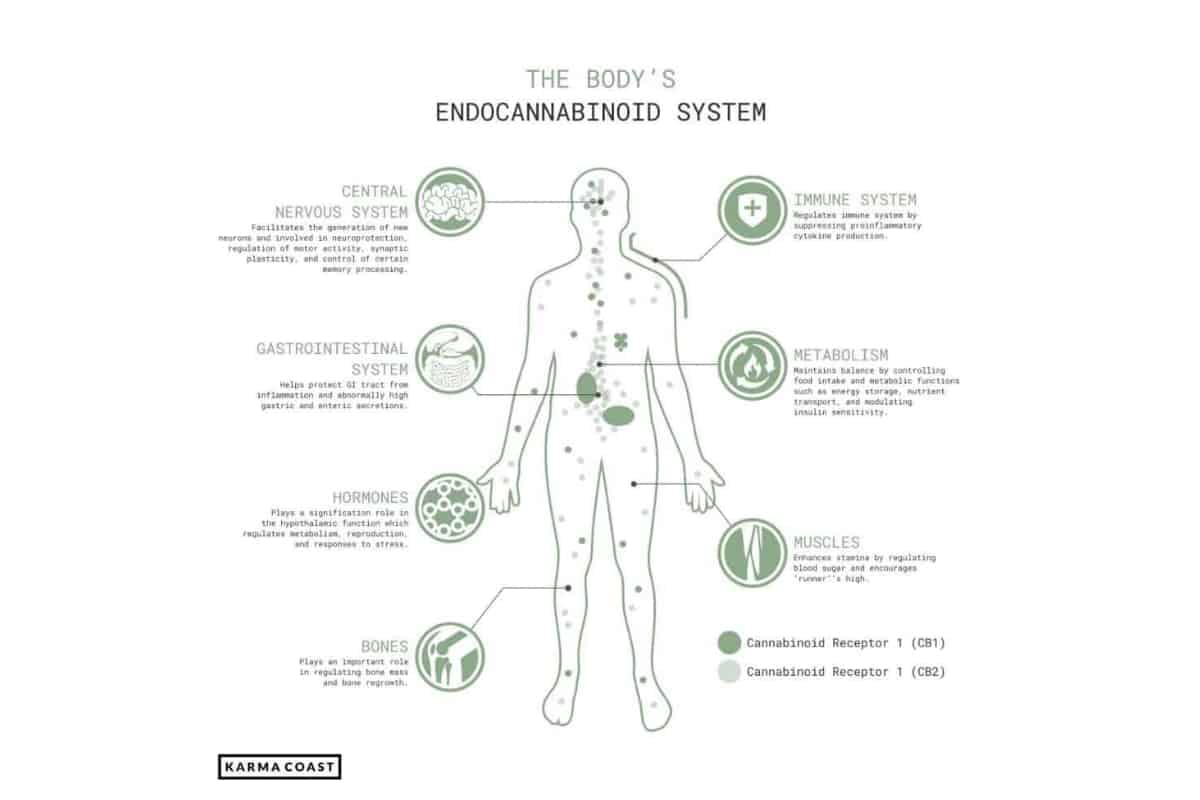
For those of you new to this, the endocannabinoid system is a major physiological system in the human body. Actually, it’s in the body of pretty much every animal – vertebrate and invertebrate, from your pet dog to a sea squirt. It’s made up of a sprawling network of receptors, present in every skin cell, your muscles, joints, all organs, within all other physiological systems, and even in your mitochondrial cell walls.
In essence, this system is in the very fabric of your being. And, to activate these receptors, we produce neurotransmitters called Endocannabinoids.
It’s these Endocannabinoids, which are synthesised and released on demand as and when the body needs rebalancing, that cannabinoids (from the cannabis plant, such as THC and CBD) mimic and support.
But what are Endocannabinoids?
What are Endocannabinoids?
The two endocannabinoids we currently know most about are called Anandamide and 2-AG. Anandamide is named after Ananda – the Sanskrit word for ‘bliss’, while the less snazzy named 2-AG is largely responsible for the sensation of an orgasm.
As you can probably guess, the presence of these lovely little chemical messengers make us feel pretty great. But there’s a lot more to it than that.
Anandamide – the Bliss Molecule
When you wiggle your finger, then stop again. When you push yourself during a workout and you body needs a boost to get through. When your mind and body needs equilibrium restored in any way – it’s endocannabinoids that will get you there.
Anandamide is one such endocannabinoid that is produced in the brain, and it’s role is well-established in regulating stress, pain, appetite, pleasure and reward responses. It’s also believed to play a key role in ovulation, conception and fetal development, as well as being present in breast milk.
Cannabinoid experts have described Anandamide as being a sort of ‘gatekeeper for stress’, as appropriate levels of this Endocannabinoid in the brain also help to mediate the fight or flight response, helping you to keep your cool until it might actually be beneficial to trigger survival mode.
2-AG
Although it’s Anandamide that often gets all the attention, fellow endocannabinoid, 2-AG, is just as important. In fact, this endocannabinoid is naturally present in the body at considerably higher levels than Anandamide. Hundreds of thousands times higher!
Unlike Anandamide, which only partially activates endocannabinoid receptors, 2-AG fully activates them to help the body maintain and regain homeostasis.
Research into endocannabinoids is ongoing, but so far studies have found that 2-AG can help reduce pain and inflammation, can help control spasms, can be neuroprotective, has anti-depressant and anxiolytic effects, and can reduce the strength of the pain signals being sent. It’s also thought that a huge rush of 2-AG might be what creates the sensation of arousal and orgasm!
What is an Endocannabinoid deficiency?
There are numerous ways to keep your Endocannabinoid levels up, including yoga, meditation, taking a regular dose of CBD oil, exercising, and even high quality dark chocolate. But what happens if your Endocannabinoids become depleted
Endocannabinoid Deficiency is a term coined by world-leading cannabinoid researcher, Dr Ethan Russo, who was the first to propose that a lack of Endocannabinoids in the body may be the root cause of numerous treatment resistant conditions. These include IBS, migraines, fibromyalgia and, as revealed in more recent research, bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
In short, if your endocannabinoid levels are low, then your body is unable to regain, or maintain, balance. Fortunately, cannabinoids provide the perfect supplement.

CBD and Endocannabinoids
You may be wondering, what have endocannabinoids got to do with CBD? As the name suggests, quite a lot. Endocannabinoids (and the endocannabinoid system) were actually discovered while scientists were researching the effects of cannabinoids (from cannabis) on the body.
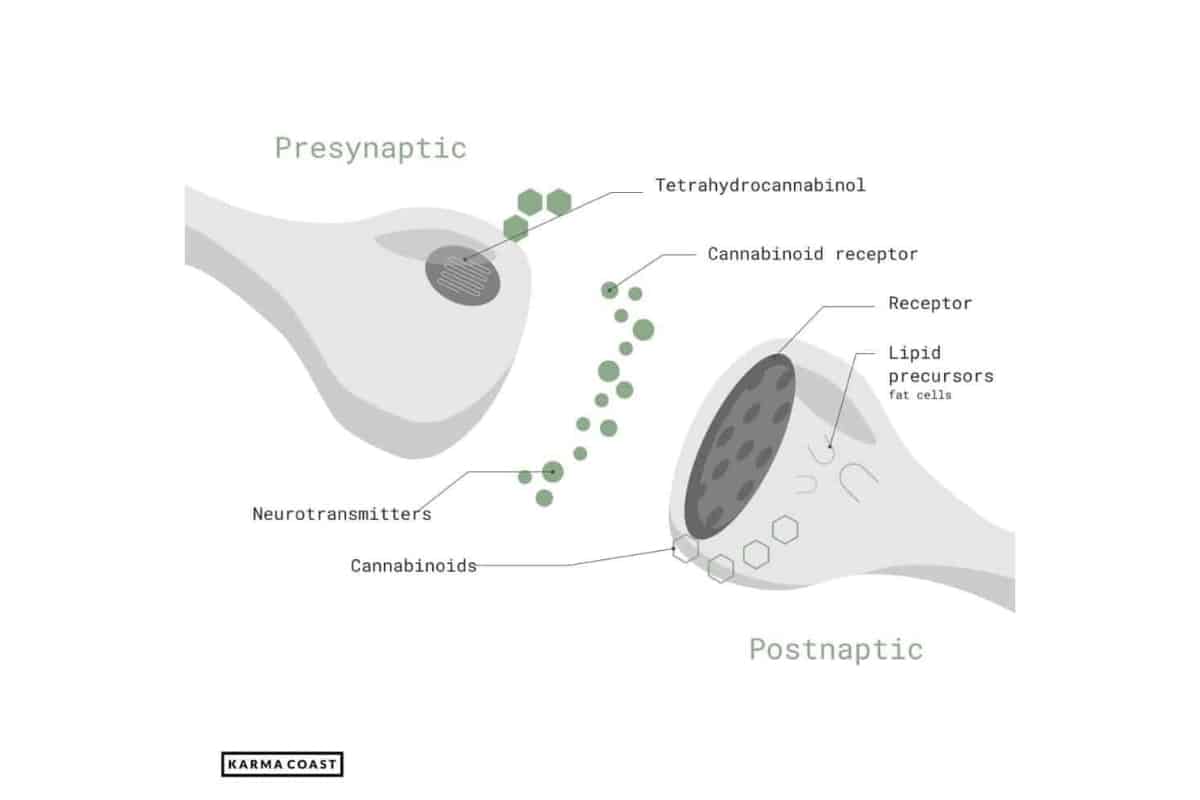
The main psychoactive molecule in cannabis, THC, mimics Anandamide almost exactly, fitting like a lock and key into endocannabinoid receptors. CBD, on the other hand, works in an entirely different way, supporting the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting the enzymes which ordinarily break down endocannabinoids (which don’t usually hang around long). This then increases production and overall levels of endocannabinoids in the body.
We’re learning more about the endocannabinoid system and the importance of endocannabinoids in just about every function every day, which is giving us transformative insight into how the body works. Want to know more about your endocannabinoid system? Take a look at our ‘Insights’ page.
Share This Post

